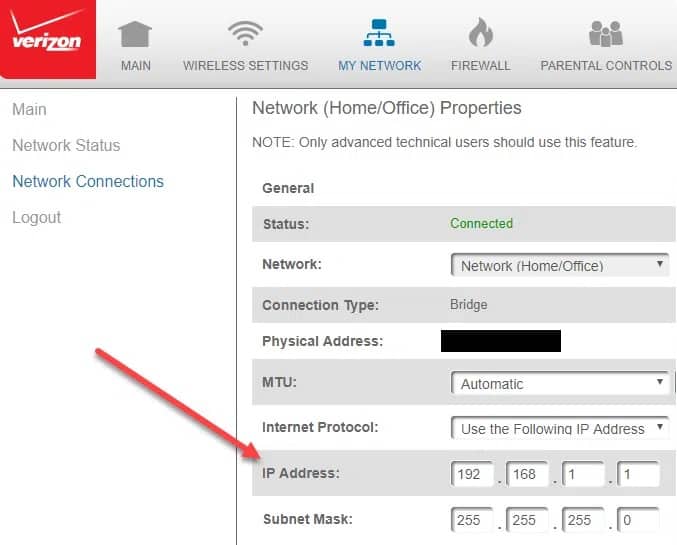
If you’ve ever wondered about the Default IP Address of your wireless router, it’s because it’s always going to be one of two numbers: 192 or 1. Having worked in IT my entire career, it bothered me that I hadn’t given attention to something that was right in front of me.
192.168.0.1 Default Router IP Address
So, why do the vast majority of routers make use of this particular address space? In reality, it’s pretty simple to do. Because the IP address cannot be routed, this is the reason for this error. Therefore, there is no need for an Internet Service Provider to assign a non-routable IP address, also known as a private IP address.
Certain IP address ranges aren’t publicly routed on the Internet, although some claim all IP addresses are routable. Before being connected to the Internet, they must first pass through a NAT gateway or a proxy server to get there.
Because an ISP typically only assigns one public IP address to a location, private IP addresses are commonly used in large and small business networks. Because the number of IPv4 addresses is rapidly diminishing, we must increasingly rely on private IP addresses. Every device will have a public IP address when IPv6 is fully implemented, but that time is still far away.
To connect multiple devices with a single public IP, a NAT (Network Address Translation) gateway converts all private IP addresses to the public IP before sending them to the Internet. Therefore, all computers on your local network have private IP addresses distributed by your NAT device (DHCP server).
Officially, three private IP address ranges have been defined by the IANA in RFC 1918:
|
IP address range |
Number of Addresses |
Class |
| 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 |
16,777,216 |
Class A |
| 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 |
1,048,576 |
Class B |
| 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 |
65,536 |
Class C |
One of these three IP address ranges is used by every private network in the world. The number of available addresses in that range determines the class. Therefore, it is only necessary for huge organizations with hundreds of interconnected networks to use Class A, with over 16 million usable addresses.
Most routers come pre-configured with a Class C IP address because they can still handle over 65,000 IP addresses, which is more than enough for almost any home or small business.
The router’s default IP address is 192.168.0.1, making it the first address in the Class C network that can be used. However, more brands have started to use 192.168.1.1 as the default IP address in recent years, possibly because it is easier to remember. Notably, the default IP address can be changed to a Class B or Class A network IP address without affecting the system’s functionality.
The only difference between private IP ranges is the number of available addresses.
The 1.0.0.0/8 and 2.0.0.0/8 private IP address ranges aren’t being used, either. You may have also seen 169.254.x.x/16 and 127.x.x.x/8 as private IP addresses. APIPA addresses and loopback addresses are the terms used to describe these two types of addresses.
ALSO READ: WMI Provider Host
Unless DHCP is unavailable, APIPA addresses are never used. Instead, IP addresses in the range of 169.254.0.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 will be automatically assigned to the devices. Thus, even if no DHCP server or IP addresses are manually assigned, devices can still communicate with one another.
All network cards have a loopback address that’s used for testing.
Final Words
Now you know why routers have IP addresses such as 192.168.0.1 or 10.10.1, for example. As a result, if you find any errors in my explanation, please let me know in the comments section below!